Aim: Implementing Diffie Hellman Key Exchange Algorithm
Theory:
- Whitefield Diffie and Martin Hellman devised an solution to the problem of key agreement or key exchange in 1976.
- This solution is called as Diffie-Hellman key exchange / Agreement Algorithm.
- The two parties who want to communicate securely can agree on a symmetric key using this technique.
- This key then is used for encryption and decryption.
- The Diffie-Hellman key exchange algorithm can be used only for key agreement but not for encryption or decryption of messages.
Source code:
import java.util.*;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class DiffieHellman {
final static BigInteger one = new BigInteger(“1”);
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner stdin = new Scanner(System. in );
BigInteger n;
// Get a start spot to pick a prime from the user.
System.out.println(“Enter the first prime no:”);
String ans = stdin.next();
n = getNextPrime(ans);
System.out.println(“First prime is: ” + n + “.”);
// Get the base for exponentiation from the user.
System.out.println(“Enter the second prime no(between 2 and n-1):”);
BigInteger g = new BigInteger(stdin.next());
// Get A’s secret number.
System.out.println(“Person A: enter your secret number now.i.e any random no(x)”);
BigInteger a = new BigInteger(stdin.next());
// Make A’s calculation.
BigInteger resulta = g.modPow(a, n);
// This is the value that will get sent from A to B.
// This value does NOT compromise the value of a easily.
System.out.println(“Person A sends ” + resulta + ” to person B.”);
// Get B’s secret number.
System.out.println(“Person B: enter your secret number now.i.e any random no(y)”);
BigInteger b = new BigInteger(stdin.next());
// Make B’s calculation.
BigInteger resultb = g.modPow(b, n);
// This is the value that will get sent from B to A.
// This value does NOT compromise the value of b easily.
System.out.println(“Person B sends ” + resultb + ” to person A.”);
// Once A and B receive their values, they make their new calculations.
// This involved getting their new numbers and raising them to the
// same power as before, their secret number.
BigInteger KeyACalculates = resultb.modPow(a, n);
BigInteger KeyBCalculates = resulta.modPow(b, n);
// Print out the Key A calculates.
System.out.println(“A takes ” + resultb + ” raises it to the power ” + a + ” mod ” + n);
System.out.println(“The Key A calculates is ” + KeyACalculates + “.”);
// Print out the Key B calculates.
System.out.println(“B takes ” + resulta + ” raises it to the power ” + b + ” mod ” + n);
System.out.println(“The Key B calculates is ” + KeyBCalculates + “.”);
}
public static BigInteger getNextPrime(String ans) {
BigInteger test = new BigInteger(ans);
while (!test.isProbablePrime(99))
test = test.add(one);
return test;
}
}
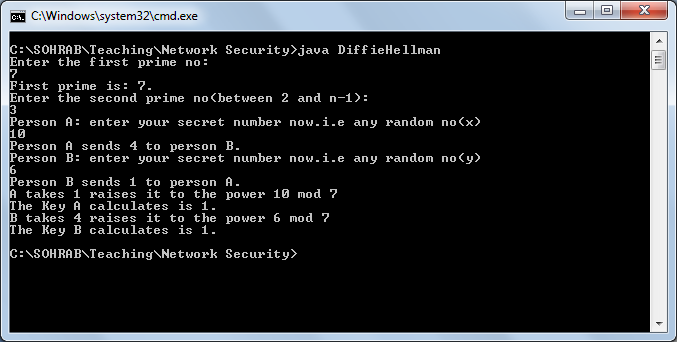
Output: